Financial Stability Report. December 2024
Poland’s financial system is stable and the banking sector, which is its key element, remains resilient to shocks.
Banks’ substantial capital surpluses create favourable conditions for the activation of the positive neutral countercyclical capital buffer, while at the same time allowing room for lending growth. The growth rate of lending remains low, which stems mainly from limited demand for credit.
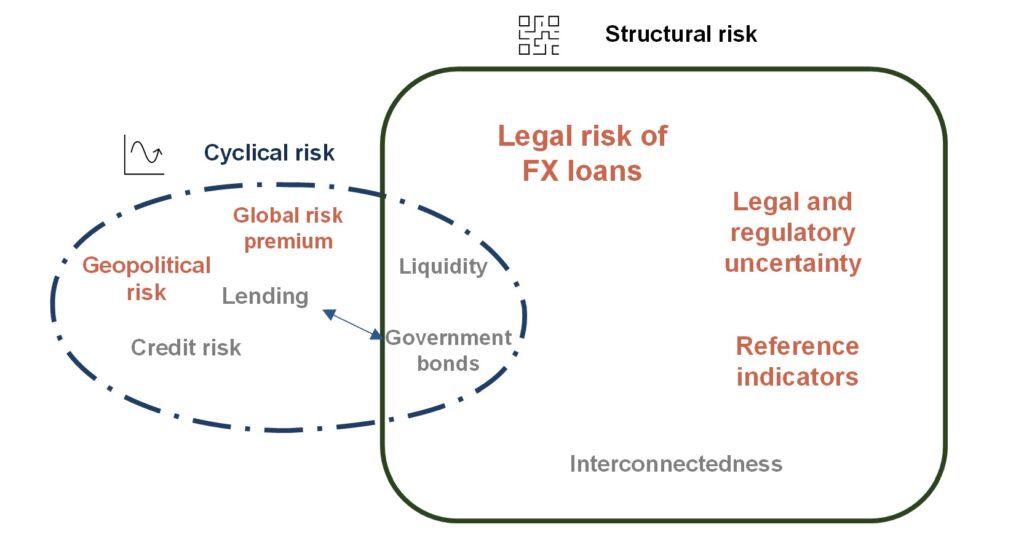
Key risks in the financial system are structural and primarily associated with legal risk and regulatory risk. Uncertainty related to these risks may weigh on the banks’ propensity to finance the private sector, especially households. The portfolio of FX housing loans has so far been the main source of costs for the banking sector. High nominal income generated by banks has recently allowed them to increase the pace at which they create legal risk provisions, thanks to which the size of future costs will be substantially smaller.
Traditional banking risks, including credit risk, liquidity risk, interest rate risk and FX risk, remain moderate and do not put financial stability in Poland at risk.
The consistent reform of interest rate benchmarks is an important condition for the stable functioning of the financial system in the future.
In the opinion of Narodowy Bank Polski, the implementation of the recommendations listed below will support the maintenance of domestic financial stability.
1. Reduction of legal and regulatory risks
Both public and private actors should consider taking proportionate actions related to consumer protection. Amending the Act on Consumer Credit should aim to modify the existing provisions on a free credit penalty.
2. Stable lending to the economy
Banks should seek to reverse the trend of a gradual decline in loans in their assets.
This action should be supported by reducing the negative external stimuli that affect the supply of credit. A modification of the tax on assets would be conducive to increasing credit availability.
3. Reform of interest rate benchmarks
Efforts should be made to ensure the unquestionable quality of the input data of the index which is to ultimately replace the WIBOR.
4. Settlements in FX housing loan cases
Banks should continue the process of reaching settlements with borrowers in FX housing loan cases.
5. Compliance with the MREL with debt instruments
Bank should continue to increase the share of eligible debt instruments in the MREL requirement for coverage of the entire amount for recapitalisation.
6. The Long-term Funding Ratio
The systemic effects of the scheduled introduction of the Long-term Funding Ratio should be monitored.
7. Activation of shareholders of the cooperative banking sector
The cooperative banking sector should step up actions aimed at reversing the negative trend in the number of shareholders.
8. Adequate assessment of insurance company solvency and the supply of longevity risk hedging products
In making their solvency assessments, it would be appropriate for insurance companies to consider the risk arising from a high share of expected profits included in future premiums in own funds and from double gearing of capital.
It is desirable that life insurance companies allocate a portion of their profits to develop insurance products that enable the hedging of longevity risk.
9. Seeking to reduce the mismatch between assets and liabilities in the investment fund sector
It would be appropriate to take effective action aimed at reducing the liquidity mismatch between assets and liabilities of open-ended investment funds.